Revenue recognition is a cornerstone of financial reporting, directly impacting an entity’s financial health and stakeholder trust. IFRS 15, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, revolutionizes the approach to revenue recognition by introducing a uniform framework applicable across all industries. This article explores the five-step model at the heart of IFRS 15, its industry implications, challenges, and benefits.
The Five-Step Model of IFRS 15
IFRS 15 establishes a five-step framework to ensure consistent and transparent revenue recognition practices:
Step 1: Identify the Contract with the Customer
A contract is an agreement between two or more parties that creates enforceable rights and obligations. For a contract to qualify under IFRS 15, it must:
- Be approved by all parties.
- Define the rights of the parties involved.
- Specify payment terms.
- Be expected to result in the transfer of goods or services.
Step 2: Identify the Performance Obligations
Performance obligations are promises to transfer distinct goods or services to the customer. A good or service is distinct if:
- The customer can benefit from it independently or with other resources.
- It can be identified as separate from other contractual obligations.
Step 3: Determine the Transaction Price
The transaction price represents the amount of consideration an entity expects in exchange for fulfilling its obligations. This includes:
- Fixed and variable components.
- Adjustments for discounts, rebates, and penalties.
- Estimations of variable consideration using the expected value or most likely amount.
Step 4: Allocate the Transaction Price to Performance Obligations
When a contract includes multiple performance obligations, the transaction price is allocated based on their standalone selling prices. This ensures each obligation reflects its relative value within the contract.
Step 5: Recognize Revenue as Performance Obligations Are Satisfied
Revenue is recognized when control of goods or services is transferred to the customer. This may occur:
- Over time, if the customer benefits as the entity performs.
- At a point in time, if control is transferred at delivery.
Industry Implications
1. Telecommunications
Companies often offer bundled services, such as mobile devices with service contracts. Under IFRS 15:
- Each component is assessed separately.
- Revenue for equipment is recognized earlier based on its standalone selling price.
2. Construction
Long-term contracts require revenue recognition based on the transfer of control. This often results in revenue being recognized progressively as performance milestones are achieved.
3. Retail
Promotional offers, such as “buy two, get one free,” necessitate careful allocation of the transaction price. Each item, including the free one, contributes to the overall revenue recognized.
Challenges of IFRS 15 Implementation
1. Complex Contract Analysis
Identifying and separating performance obligations can be challenging in bundled contracts or those with variable terms.
2. Variable Consideration
Judgment is required to estimate variable consideration, such as bonuses or penalties. These estimations must reflect a probable outcome.
3. Comprehensive Disclosure Requirements
IFRS 15 demands detailed disclosures about:
- The nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue.
- Revenue recognized from contracts with customers.
Benefits of IFRS 15
1. Enhanced Transparency
The standardized framework improves comparability and clarity in financial reporting.
2. Alignment Across Industries
IFRS 15 creates a consistent approach, enabling stakeholders to better assess financial performance.
3. Focus on Customer Contracts
By emphasizing the substance of agreements, IFRS 15 ensures revenue reflects actual business activity.
Example: Sale of Software Licenses with Subsequent Updates under IFRS 15
The application of IFRS 15 to a scenario involving the sale of software licenses with subsequent updates requires a detailed analysis of the contract and the allocation of revenue. This example illustrates the five-step model in practice.
Scenario
TechSolutions Inc. sells a software license for $10,000, which allows the customer perpetual use of the software. The company also provides free updates and technical support for one year. After the first year, the customer can renew the updates and support for $2,000 annually.
Key Considerations:
- The contract involves multiple components: the software license and one year of updates/support.
- Revenue must be allocated to each performance obligation.
Step 1: Identify the Contract with the Customer
The customer enters into a contract with TechSolutions Inc. that:
- Provides a perpetual license for the software.
- Includes free updates and support for one year.
The contract meets the criteria of IFRS 15, as it creates enforceable rights and obligations and includes clear payment terms.
Step 2: Identify the Performance Obligations
There are two distinct performance obligations:
- Software License: A perpetual license that the customer can use immediately.
- Updates and Support: Ongoing services that provide software improvements and technical assistance over one year.
The software license is a distinct good because the customer can benefit from it independently, while the updates and support are separate services provided over time.
Step 3: Determine the Transaction Price
The total transaction price is $10,000 for the bundle, including the license and one year of updates/support.
Step 4: Allocate the Transaction Price to Performance Obligations
TechSolutions Inc. determines the standalone selling prices:
- Software License: $9,000
- Updates and Support: $3,000 (based on the renewal price of $2,000 annually and an estimated value for the initial year of service).
Using the standalone selling prices, the transaction price is allocated as follows:
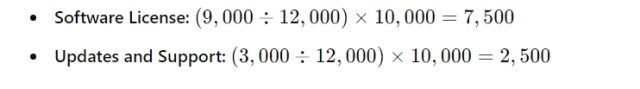
Step 5: Recognize Revenue as Performance Obligations Are Satisfied
- Software License:
- The license is delivered immediately, and control transfers to the customer upon delivery.
- Revenue of $7,500 is recognized at the time of delivery.
- Updates and Support:
- These services are provided over one year, satisfying the performance obligation over time.
- Revenue of $2,500 is recognized on a straight-line basis over the 12 months, at $208.33 per month.
Journal Entries
At the Start of the Contract (Delivery of License):
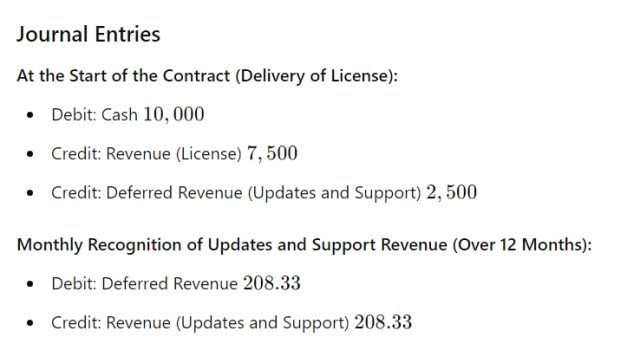
Summary
This example demonstrates how IFRS 15 ensures revenue reflects the actual delivery of goods and services. By allocating the transaction price based on standalone selling prices and recognizing revenue as obligations are satisfied, businesses provide stakeholders with a transparent view of their revenue streams.
IFRS 15 and Its Transformational Impact
IFRS 15 is not just a technical accounting standard; it is a transformative framework that reshapes how businesses approach revenue recognition. By providing a clear, structured, and principles-based methodology, the standard ensures that revenue reporting reflects the actual economic activity and value exchange between entities and their customers. This level of consistency and transparency is critical in today’s interconnected and globalized business environment, where comparability across industries and jurisdictions is paramount.
The five-step model introduced by IFRS 15 simplifies the complexity of revenue recognition while addressing the nuances of various industries. This approach aligns revenue recognition practices across sectors, fostering comparability and uniformity. Stakeholders—ranging from investors to regulators—can now trust that reported revenues are consistent with the underlying performance of a business, enhancing decision-making and confidence in financial statements.
Overcoming Challenges and Unlocking Opportunities
Adopting IFRS 15 requires businesses to navigate certain challenges, such as:
- Contract Analysis: Dissecting and understanding complex contracts to identify distinct performance obligations.
- Variable Consideration: Estimating uncertain revenue components with precision and justifiable methodologies.
- Enhanced Disclosures: Meeting the comprehensive disclosure requirements to provide stakeholders with a detailed understanding of revenue streams.
While these challenges may appear daunting, they also present opportunities for businesses to:
- Strengthen Internal Processes: Implementation often necessitates revisiting and refining contract management and accounting systems, resulting in more efficient operations.
- Improve Stakeholder Communication: Detailed and transparent reporting enhances the narrative around a company’s financial performance, boosting credibility and investor relations.
- Gain Strategic Insights: The in-depth analysis required by IFRS 15 often uncovers valuable data, enabling better forecasting, pricing strategies, and customer relationship management.
Why Businesses Must Prioritize IFRS 15 Compliance
Failing to embrace IFRS 15 can have serious repercussions, including financial misstatements, regulatory penalties, and loss of stakeholder trust. Businesses must view this standard as more than a compliance exercise. It is a tool for aligning financial reporting with business strategy, ensuring that reported revenue is an accurate reflection of the entity’s value proposition to its customers.
Future-Proofing Financial Reporting
The adoption of IFRS 15 positions businesses to navigate the complexities of modern commerce more effectively. As industries evolve—driven by technological advancements, global competition, and shifting customer expectations—the ability to accurately and transparently report revenue will remain a cornerstone of sustainable success. Businesses that fully embrace IFRS 15 will find themselves better equipped to adapt to future changes in accounting standards and regulatory frameworks.
Final Thoughts
IFRS 15 is a game-changer because it fosters clarity, consistency, and comparability across the global business landscape. While the transition to this framework may present initial challenges, the long-term benefits of enhanced financial reporting far outweigh the effort. Entities that invest in understanding and applying IFRS 15 are not just complying with a standard—they are building a foundation of trust and credibility in their financial reporting. In a world where accurate information drives competitive advantage, IFRS 15 stands as a vital pillar of sound financial management and stakeholder confidence.
Next Step!
“Embrace BIG FIRM capabilities without the big firm price at Dawgen Global, your committed partner in carving a pathway to continual progress in the vibrant Caribbean region. Our integrated, multidisciplinary approach is finely tuned to address the unique intricacies and lucrative prospects that the region has to offer. Offering a rich array of services, including audit, accounting, tax, IT, HR, risk management, and more, we facilitate smarter and more effective decisions that set the stage for unprecedented triumphs. Let’s collaborate and craft a future where every decision is a steppingstone to greater success. Reach out to explore a partnership that promises not just growth but a future beaming with opportunities and achievements.
✉️ Email: [email protected] 🌐 Visit: Dawgen Global Website
📞 Caribbean Office: +1876-6655926 / 876-9293670/876-9265210 📲 WhatsApp Global: +1 876 5544445
📞 USA Office: 855-354-2447
Join hands with Dawgen Global. Together, let’s venture into a future brimming with opportunities and achievements


