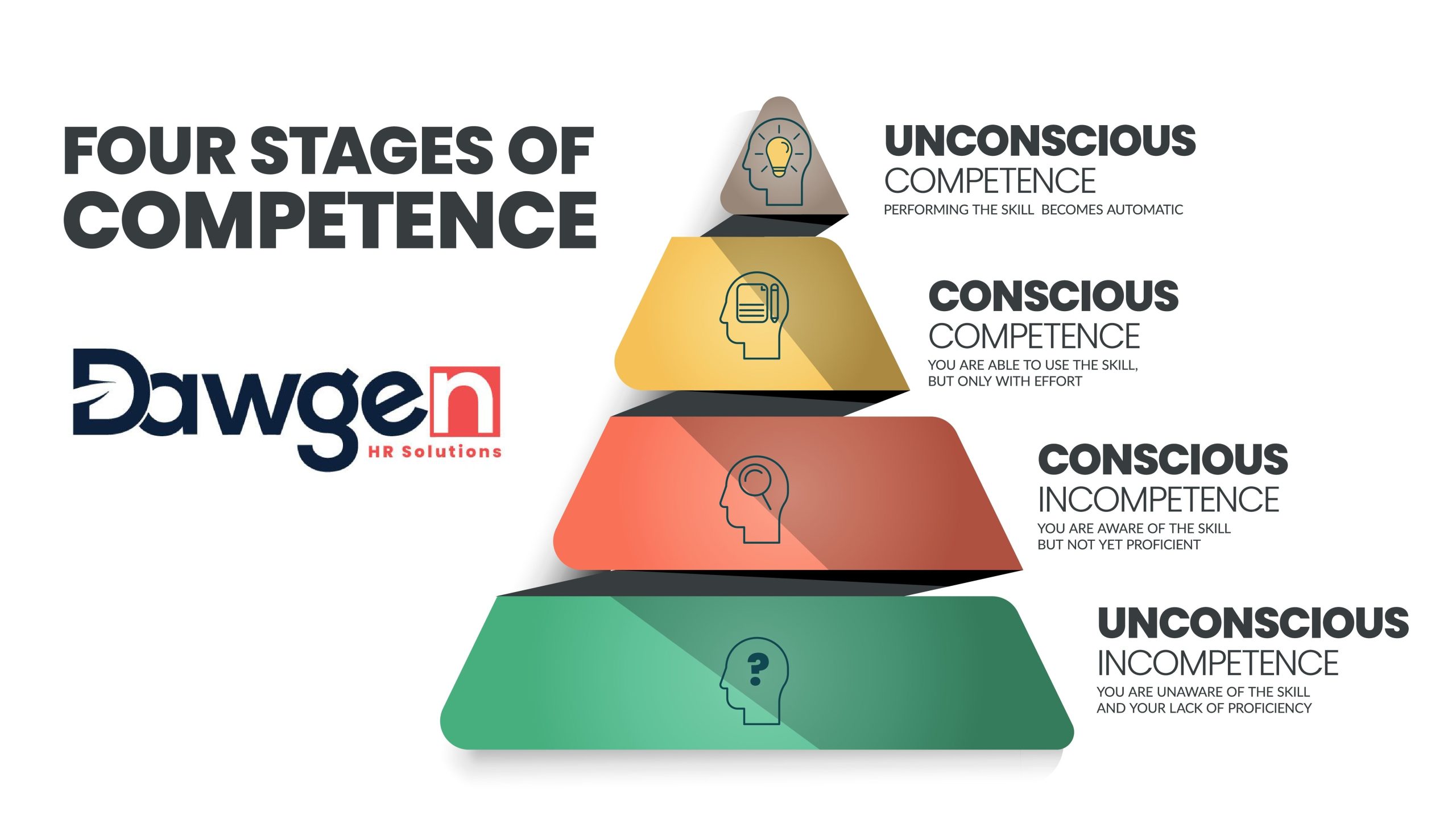
In the fast-evolving landscape of business, the concept of competency has become a cornerstone of Human Resource Management (HRM). As Dr. Dawkins Brown, Executive Chairman of Dawgen Global, aptly puts it, “In a world where change is constant, the currency of competency reigns supreme.” This article delves into the multifaceted role of Competency Alignment in HRM, elucidating its significance and application in modern organizational settings.
1. Understanding “COMPETENCY”
Competency, in the HRM context, refers to a blend of skills, knowledge, and behaviors that enable individuals to perform their roles effectively. It’s a measure not just of what one knows, but how they apply this knowledge in various situations.
2. Competencies as Inputs
Viewed as inputs, competencies form the bedrock upon which employees build their performance. They represent the foundational elements necessary for success in specific roles.
3. Key Behavior Indicators
Key Behavior Indicators (KBIs) are observable actions or behaviors that demonstrate the presence of a competency. They offer tangible evidence of how competencies manifest in the workplace.
4. Competency Model
A Competency Model is a structured framework that outlines the required competencies for a specific role, department, or organization. It serves as a guide for both hiring and development.
5. Competency – Broad Categories
Competencies are often categorized broadly into core, leadership, and functional competencies, each relevant to different roles and levels within an organization.
6. Traditional Job Analysis Vs Competency Approach
Traditional job analysis focuses on tasks and duties, while the competency approach emphasizes the skills and behaviors required to perform these tasks effectively.
7. Distinguishing Superior From Satisfactory Performance
Competency-based approaches help in differentiating between superior and merely satisfactory performance by identifying the specific competencies that lead to exceptional results.
8. Behavior Indicators Based on Outstanding Performance
Behavior indicators are developed based on the study of what outstanding individuals actually do, offering a practical and observable measure of competency.
9. Competencies as Behavior Specific
Competencies are specific in their behavioral orientation, making it easier for managers to identify, measure, and develop them in their teams.
10. Holistic Application
The competency framework is applied holistically, encompassing various aspects of HRM from recruitment to performance management.
11. Alignment of HR Systems
Aligning HR systems with competencies ensures that all HR functions are streamlined and focused on developing key skills and behaviors.
12. Competency-Based Recruitment
This approach to recruitment focuses on identifying candidates who demonstrate the competencies necessary for success in the role.
13. Competency-Based Performance Appraisal
Performance appraisals based on competencies provide a more objective and comprehensive evaluation of an employee’s performance.
14. Competency-Based Training
Training programs designed around competencies ensure that employees develop the skills and behaviors that are directly relevant to their roles.
15. Competency-Based Development
Competency-based development focuses on long-term career development, aligning individual growth with organizational needs.
16. Competency-Based Pay
This pay structure rewards employees based on the demonstration and development of key competencies.
17. Competency Methodology
Competency methodology involves the systematic approach of identifying, defining, and measuring competencies within an organization.
18. Steps in Model Building
Building a competency model involves steps like role profiling, competency identification, and framework development.
19. Data Collection Methods
Data collection for competency modeling can include interviews, surveys, and job observations.
20. Competency Mapping Models
These models provide a visual representation of the required competencies and their relationship to various roles and functions within the organization.
21. Competency Mapping Process
This process involves identifying key competencies for each role and mapping them across the organization to ensure alignment and coherence.
Conclusion
Competency Alignment in HRM represents a strategic and holistic approach to managing human resources. By focusing on the development and application of key competencies, organizations can enhance their performance, foster continuous learning, and remain competitive in the dynamic business environment. As underscored by the insights of Dr. Dawkins Brown, mastering the art of competency alignment is crucial for organizational success in the contemporary business landscape.
Next Step!
“Embrace BIG FIRM capabilities without the big firm price at Dawgen Global, your committed partner in carving a pathway to continual progress in the vibrant Caribbean region. Our integrated, multidisciplinary approach is finely tuned to address the unique intricacies and lucrative prospects that the region has to offer. Offering a rich array of services, including audit, accounting, tax, IT, HR, risk management, and more, we facilitate smarter and more effective decisions that set the stage for unprecedented triumphs. Let’s collaborate and craft a future where every decision is a steppingstone to greater success. Reach out to explore a partnership that promises not just growth but a future beaming with opportunities and achievements.
✉️ Email: [email protected] 🌐 Visit: Dawgen Global Website
📞 Caribbean Office: +1 876 926 5210 📲 WhatsApp Global: +1 876 493 4923
Join hands with DawgenGlobal. Together, let’s venture into a future brimming with opportunities and achievements.

