In the cutthroat world of business, understanding the competitive landscape is not just beneficial—it’s essential for survival and success. As Dr. Dawkins Brown, the executive chairman of Dawgen Global, aptly puts it, “In the realm of business, ignorance of your competition is not bliss—it’s a pathway to obsolescence.” To thrive, businesses must employ strategic frameworks to dissect and dominate their market. This article delves into four pivotal frameworks that empower businesses to analyze their competitive environment and carve out a sustainable competitive advantage: Porter’s Five Forces, Industry Lifecycle Analysis, Strategic Groups Analysis, and Critical Success Factors.
1. Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces framework is a cornerstone of strategic analysis, offering a comprehensive view of the competitive forces shaping industry dynamics.
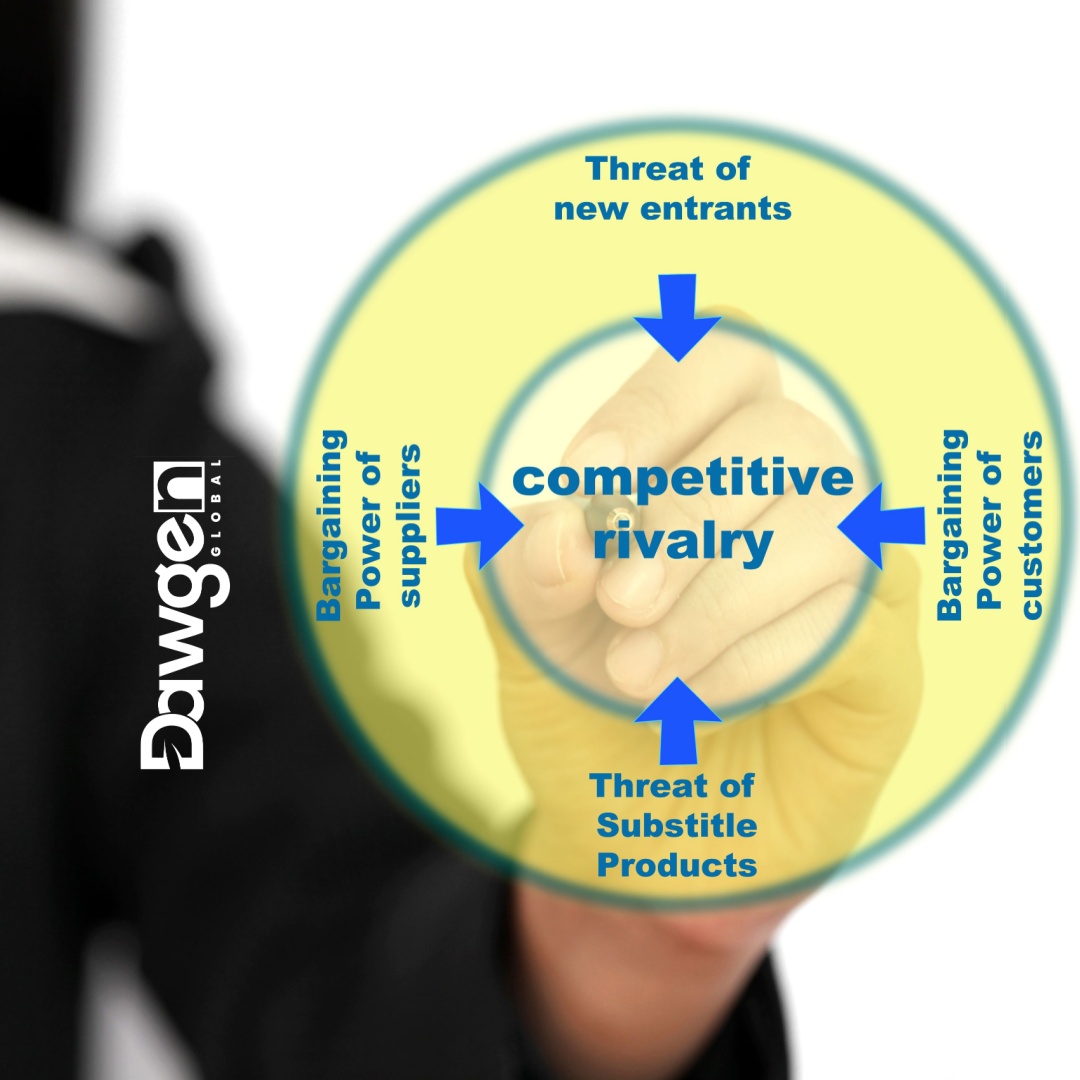
By examining each force in detail, businesses can develop strategies to enhance their competitive position and profitability.
1. Industry Rivalry
- Characteristics: This force examines the intensity of competition among existing firms within the industry. High rivalry limits profitability as companies engage in price wars, marketing battles, and product innovations.
- Key Factors: Number of competitors, rate of industry growth, product or service differentiation, and switching costs for customers.
- Strategies: Companies can focus on building strong brand loyalty, creating unique value propositions, and improving customer service to stand out from competitors and mitigate the effects of intense rivalry.
2. Threat of New Entrants
- Characteristics: New entrants increase competition and can erode existing firms’ market share and profitability. The easier it is for new companies to enter the industry, the greater the threat.
- Key Factors: Barriers to entry such as capital requirements, economies of scale, access to distribution channels, and regulatory policies.
- Strategies: Firms can deter new entrants by capitalizing on economies of scale, establishing strong brand recognition, and developing close relationships with suppliers and customers.
3. Threat of Substitute Products or Services
- Characteristics: Substitutes offer alternative solutions to the same customer needs, which can limit the potential of firms within the industry to raise prices or secure customer loyalty.
- Key Factors: Availability of substitute products, price-performance ratio of substitutes, and buyer’s willingness to switch.
- Strategies: Enhancing product differentiation, increasing switching costs, and continuous innovation can help firms reduce the threat of substitutes.
4. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Characteristics: Powerful suppliers can exert influence by raising prices, reducing the quality of goods, or limiting the availability of products, which can squeeze profitability.
- Key Factors: Number of suppliers, uniqueness of service or product, presence of substitute inputs, and cost of changing suppliers.
- Strategies: Developing multiple supply sources, building strong relationships with suppliers, or integrating supply chains can help reduce supplier power.
5. Bargaining Power of Buyers
- Characteristics: When buyers have significant power, they can demand lower prices, higher quality, or more services, impacting industry profitability.
- Key Factors: Number of buyers, size of each order, differences between competitors, and price sensitivity.
- Strategies: Differentiating products, creating switching costs, and enhancing relationships with customers can mitigate buyer power.
Applying Porter’s Five Forces
To effectively leverage this framework, businesses should conduct a comprehensive analysis of each force, understand the underlying factors, and develop tailored strategies to address each area. This analysis not only helps in identifying the current competitive intensity but also aids in anticipating future shifts in the competitive landscape.
Porter’s Five Forces framework empowers businesses to make strategic decisions that align with the external market environment, ensuring that they are better positioned to capitalize on opportunities and defend against potential threats. By continually assessing these forces, companies can maintain a dynamic strategy that adapts to evolving industry conditions, fostering long-term sustainability and success.
2. Industry Lifecycle Analysis
Industry Lifecycle Analysis is a crucial framework that helps businesses understand the evolutionary stages of their industry, enabling them to align their strategies with the prevailing market dynamics. Each stage of the lifecycle—introduction, growth, maturity, and decline—poses unique challenges and opportunities that require distinct strategic responses.
Detailed Exploration of Each Stage
- Introduction Stage
- Characteristics: This phase is marked by the introduction of new products or services, often spurred by innovation. The market size is small, customer awareness is low, and the initial cost of entry is high.
- Challenges: Companies face challenges like establishing market presence, attracting early adopters, and managing high costs associated with product development and marketing.
- Opportunities: There’s significant opportunity for establishing brand loyalty and becoming a market leader. Early entrants can set industry standards and influence customer preferences.
- Strategic Focus: Strategies often revolve around product development, market education, and building distribution channels. Investment in marketing and customer feedback is critical to refine product offerings.
- Growth Stage
- Characteristics: This stage features rapid market expansion, increasing customer adoption, and a rise in competition as more players enter the market.
- Challenges: The primary challenges include scaling operations, maintaining service or product quality, and differentiating from competitors.
- Opportunities: There’s a significant opportunity for market share expansion and brand establishment. Companies can also explore diversification and market segmentation.
- Strategic Focus: Strategies should focus on market penetration, improving operational efficiencies, and customer retention. It’s also a time to invest in innovation to sustain growth.
- Maturity Stage
- Characteristics: Growth slows down, the market becomes saturated, and competition is intense. Products and services become commoditized, and companies fight for market share.
- Challenges: The key challenges are to maintain market share, reduce costs, and increase operational efficiencies. Companies must also fend off competition and deal with price wars.
- Opportunities: Companies can focus on market segmentation to identify niche markets or introduce product variations. There’s also an opportunity to explore new markets or acquisitions.
- Strategic Focus: The focus should be on cost control, process optimization, customer loyalty programs, and exploring new markets or product innovations to sustain revenue.
- Decline Stage
- Characteristics: The industry experiences a downturn in demand, possibly due to technological advancements, shifts in consumer preferences, or external economic factors. Consolidation becomes prevalent.
- Challenges: Companies face declining sales, excess capacity, and the need to make difficult decisions regarding exiting the market or pivoting.
- Opportunities: There are opportunities for acquiring distressed assets at a lower cost, divesting non-core businesses, and pivoting to emerging markets or sectors.
- Strategic Focus: Strategies may include cost reduction, divestiture, product or market pivoting, and exploring strategic partnerships or acquisitions to exit the industry gracefully or transition into new markets.
Applying Industry Lifecycle Analysis
Understanding where an industry stands in its lifecycle allows businesses to make informed strategic decisions. For instance, a company in a mature industry might focus on cost leadership and market segmentation, while one in a growth industry might prioritize investment in innovation and market expansion. Regularly assessing the industry’s lifecycle stage helps companies stay aligned with market conditions and adapt their strategies to maintain competitiveness and drive growth.
In conclusion, Industry Lifecycle Analysis is not just about understanding the current stage of the industry but also about anticipating future trends and preparing for them. By adapting to the lifecycle stage, companies can not only survive but thrive, even in the face of industry-wide transitions and challenges.
3.Strategic Groups Analysis
Strategic Groups Analysis is a profound tool that enables businesses to map out the competitive landscape in a structured manner, providing insights into how companies within the same industry can be segmented based on key strategic dimensions. This segmentation reveals the competitive structure of the industry and aids in the development of strategic initiatives.
Understanding Strategic Groups
A strategic group consists of industry players that adopt similar business models or strategies. These groups are formed based on several dimensions, such as:
- Market Segmentation: Companies targeting similar customers or market niches.
- Quality: Businesses offering similar quality levels, whether premium or budget.
- Pricing Strategies: Organizations that price their products or services comparably.
- Geographic Coverage: Companies operating in the same regions or types of markets.
- Distribution Channels: Businesses using similar channels to reach their customers.
- Technological Adoption: Companies that are at similar stages of technological advancement or use comparable technology in their operations.
By analyzing these dimensions, companies can identify which strategic group they belong to and who their closest competitors are.
Key Benefits of Strategic Groups Analysis
- Competitor Identification and Analysis: By understanding the strategic groupings, a company can clearly identify its direct competitors and analyze their strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. This analysis can reveal competitive gaps that the company can exploit or areas where it needs to improve to remain competitive.
- Anticipating Competitor Moves: Understanding the strategic basis of different groups allows companies to anticipate potential moves by their competitors. For example, if a group is characterized by a high level of innovation, members of that group are likely to introduce new products or services more frequently.
- Market Opportunity Identification: Strategic Groups Analysis can uncover gaps in the market where no companies are currently operating, or where existing offerings are inadequate. These gaps represent potential opportunities for businesses to differentiate themselves and capture untapped market segments.
- Strategic Decision Making: By understanding the landscape of strategic groups, a company can make more informed strategic decisions, such as whether to compete head-on with companies in a particular group, target a different segment, or even shift to a different strategic group.
Implementing Strategic Groups Analysis
- Mapping Strategic Groups: The first step is to map out the strategic groups within the industry based on key dimensions. This can be visualized using multi-dimensional scaling or other statistical methods to create a visual map of the competitive landscape.
- Analyzing Group Characteristics: Each group’s characteristics should be analyzed to understand the basis of competition and the factors driving success within each group.
- Evaluating Group Dynamics: Companies should monitor changes in group dynamics, as shifts in strategies, mergers, acquisitions, or exits can alter the competitive balance within an industry.
- Identifying Strategic Opportunities: By comparing the company’s position to others within its strategic group and across other groups, management can identify strategic opportunities and threats.
In conclusion, Strategic Groups Analysis is a powerful tool that provides a nuanced understanding of the competitive forces at play within an industry. It helps businesses navigate complex market environments, enabling them to craft strategies that are finely tuned to the competitive reality of their industry.
4. Critical Success Factors (CSFs)
Critical Success Factors (CSFs) are pivotal elements or areas that a business must excel in to achieve competitive superiority and operational success. These factors are so vital that failing in one aspect can significantly hinder the overall performance and success of the company. Understanding and leveraging CSFs enable organizations to direct their focus and resources towards activities that are crucial for their success, ensuring they remain competitive and relevant in their industry.
Identifying CSFs
The process of identifying CSFs requires a thorough understanding of the industry, market trends, customer preferences, and the broader business environment. It involves a mix of qualitative and quantitative analysis, including market research, competitor analysis, and internal performance review. For different industries, the CSFs can vary greatly. For example, in the technology sector, innovation and speed to market might be key, whereas, in the retail sector, customer experience and supply chain efficiency could be more critical.
Categories of CSFs
- Industry-specific CSFs: These are factors that are vital across a particular industry. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, drug approval by regulatory bodies is a critical success factor.
- Strategy-specific CSFs: These factors are related to the company’s chosen strategic path. For instance, a company focusing on cost leadership must achieve operational efficiency as a critical success factor.
- Environmental CSFs: These include external factors that the company might not control but needs to address, such as compliance with regulatory standards or adapting to technological advancements.
- Temporal CSFs: These are time-sensitive factors that are crucial for a specific period due to various reasons, such as meeting a critical deadline for a product launch.
Utilizing CSFs to Achieve Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Alignment: Organizations need to align their strategies and operations to focus on enhancing their CSFs. This alignment ensures that the company’s efforts are concentrated on areas that will maximize its competitive edge and market performance.
- Resource Allocation: Understanding CSFs helps businesses allocate their resources more effectively, prioritizing investments in areas that will yield the highest returns and support the company’s strategic objectives.
- Performance Measurement: CSFs serve as key performance indicators that help businesses measure and track their progress towards strategic goals. Regularly monitoring these factors allows companies to make informed decisions, adapt strategies, and respond to market changes proactively.
- Differentiation: Excelling in areas identified as CSFs can differentiate a company from its competitors. This differentiation, whether through superior customer service, innovative products, or operational excellence, can become a unique selling proposition that attracts and retains customers.
Continuous Evaluation
The business environment is dynamic, with rapid changes in market conditions, consumer preferences, and technological advancements. Therefore, it’s crucial for businesses to regularly review and update their CSFs to ensure they remain relevant and aligned with the current market and organizational context.
In summary, Critical Success Factors are not just indicators of what businesses need to get right; they are the beacons that guide strategic direction, operational focus, and resource allocation. By mastering their CSFs, companies can not only navigate the competitive landscape effectively but also pave the way for sustained success and growth.
In conclusion, understanding and applying these four frameworks allows businesses to conduct a comprehensive analysis of their competitive landscape. By doing so, they can make informed strategic decisions, anticipate market shifts, and position themselves for long-term success. As highlighted by Dr. Brown’s insight, staying attuned to the competitive dynamics is not an option but a necessity in today’s fast-paced business world.
Next Step!
“Embrace BIG FIRM capabilities without the big firm price at Dawgen Global, your committed partner in carving a pathway to continual progress in the vibrant Caribbean region. Our integrated, multidisciplinary approach is finely tuned to address the unique intricacies and lucrative prospects that the region has to offer. Offering a rich array of services, including audit, accounting, tax, IT, HR, risk management, and more, we facilitate smarter and more effective decisions that set the stage for unprecedented triumphs. Let’s collaborate and craft a future where every decision is a steppingstone to greater success. Reach out to explore a partnership that promises not just growth but a future beaming with opportunities and achievements.
✉️ Email: [email protected] 🌐 Visit: Dawgen Global Website
📞 Caribbean Office: +1876-6655926 / 876-9293670 📲 WhatsApp Global: +1 876 5544445
Join hands with DawgenGlobal. Together, let’s venture into a future brimming with opportunities and achievements.

